View Settings on Google Analytics
A Google Analytics user can have up to 50 different sources or individual web pages.
Sources can have up to 25 different views that are used to analyze and report on different data. Each view can be configured exactly the way you want to see the statistics.
Creating additional views allows you to filter your statistics – for example, by goals or conversions. When creating views, keep in mind that if you create a new view, statistics for previous periods will not be displayed in the new view.
01Create new views
If you haven’t created an additional view in Google Analytics, then your default view in Google Analytics is named All Web Site Data. It’s a good idea to set it up as a Raw Data view which gives every Google Analytics user an indicator that this data is a backup data of your webpage statistics.
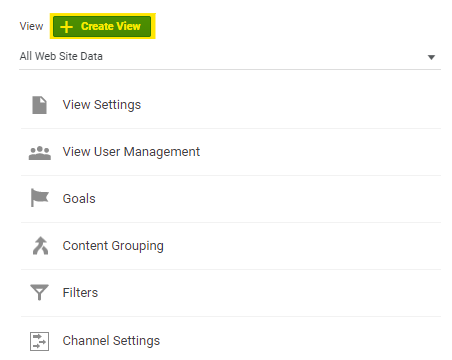
Name the new view to help you differentiate it from the baseline.
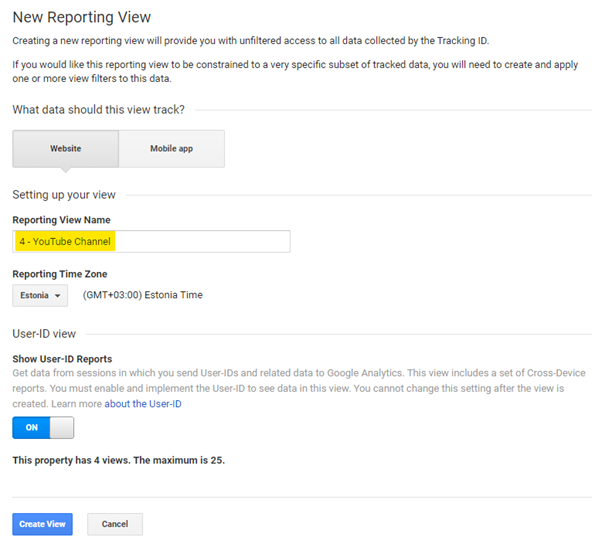
1) Production View
A view where you are constantly analyzing your data. You have pre-tested and working goals, activities, filters, etc. set up in this view.
2) Test View
A view where you can confidently test different setups before activating them Production View. For example Filters, Goals and Events.
3) Raw Data
Statistics that you are not affected by and to which you do not add any Filters, Goals, or Events. This view acts as a backup of your website’s data.
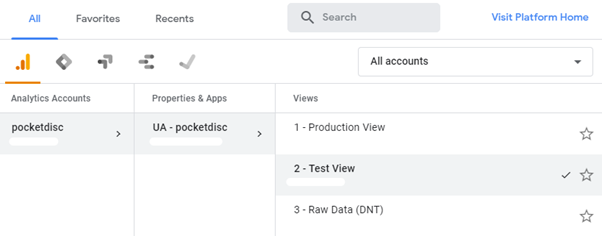
It makes sense to create a separate source for each website that your business has. For example, if you have an e-shop that sells coffee cups and you have a separate website for selling teacups, both pages should have unique Properties and Views.
If you’re required to create a Google Analytics account for your business, please register with your business email. If you create it from your own personal account, you will later have problems allocating ownership, especially in a situation where you may not work for the company in the future.
Pro tip #1
If you manage Google Analytics accounts for different companies, create a separate account for each business. This kind of user management allows you to easily share ownership with the company.

02Basic Settings
Bot Filtering
Bot Filtering helps you filter out various visits and activity from a webpage by known bots or scripts from your Google Analytics data.
This makes the data to be analyzed cleaner. NB! However, it is not recommended to do this in the Raw Data view, because as mentioned earlier, in this backup view, all data should be unchanged.
Timezone
Adding a timezone is important because it shows you daily information. If your website is operating in Estonia and the Google Analytics time zone is set to Hawaii, all of your reporting will become chaotic over time.
Activate Site Search
If your website has a search function that uses query parameters, you will be able to get an overview of the keywords searched on the website.
Site Search keyword statistics give you the opportunity to improve your user experience. This will help you understand exactly what people are looking for at your website.
Before we turn on Site Search, we need to understand how our search system works.
To do this, go to your website and use the search function. Track your URL when a search result arrives.
![]()
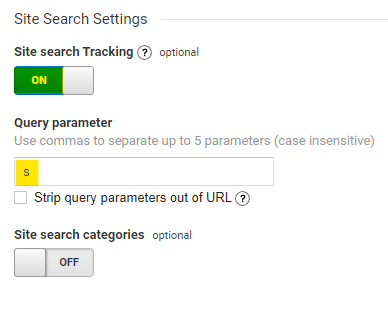
s = facebook indicates that I used search and the term that I searched for was “facebook”. Here, the search indicator was “s”. Remember this – you will need it for the next steps.
If you use an advanced search on your website, the indicator may become “advs = search + term”. In this case, the indicator is “advs”.
If both indicators are used on your website, both of these indicators must be added to the query parameter box. Site Search is activated in the View Settings section.
Click Site Search Tracking and add the indicator shown in the examples above as a query parameter. In our example, this was “s”.
Pro tip #2
If your website doesn’t use query parameters, the easiest way to gather information about search results is to reconfigure your search engine. If this is not possible, this information can be collected through filters or Google Tag Manager.
03Add filters
Add filters
Filters help isolate statistics you don’t want to add to your View. In-house statistics, which include web visits from your employees, are filtered out most often.
The easiest way to do this is to set up a filter that includes your office’s IP address. If you have multiple offices, you can separate information for multiple IP addresses from website statistics.
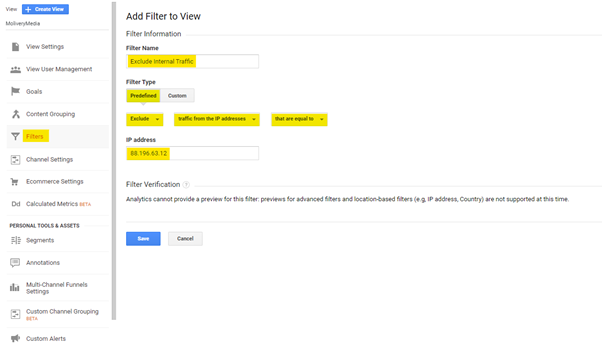
For example, you can add web traffic that contains web traffic from a specific domain or subdomain as a filter.
In web development, it’s common to add a filter that doesn’t take into account the actions taken by the developers. For example, setting up the Google Analytics conversions you want to measure would filter out Google Analytics statistics. Adding a filter will not reflect the conversion statistics tested in Google Analytics statistics.
04Seperate URL query parameters
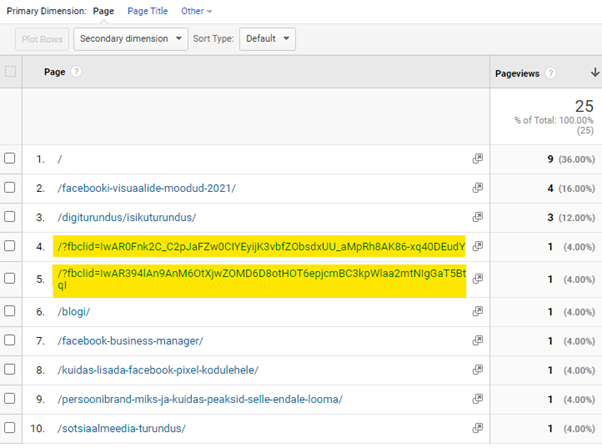
URL query parameters indicate where visitors come from or provide information about a visitor’s cart. These are very useful parameters.
However, they can confuse page-based statistics.
Google Analytics shows each unique URL separately – it’s a good idea to separate the URL query parameters to differentiate between them.
Pro tip:
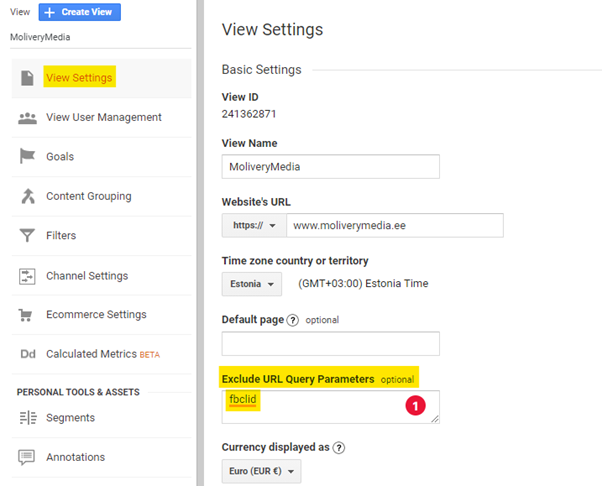
UTM parameetrid eraldatakse automaatselt URL-idest. Eralda ainult unikaalsed parameetrid, nagu näiteks see, mis näites kuvatud.
Ülemise näite puhul peaksid URL-päringu parameetri väljale lisama järgneva väärtuse:
05Copy View
The Copy View feature is a great way to create different views. Especially when you want to copy Goals, Filters, or Events from a specific view to a new view.
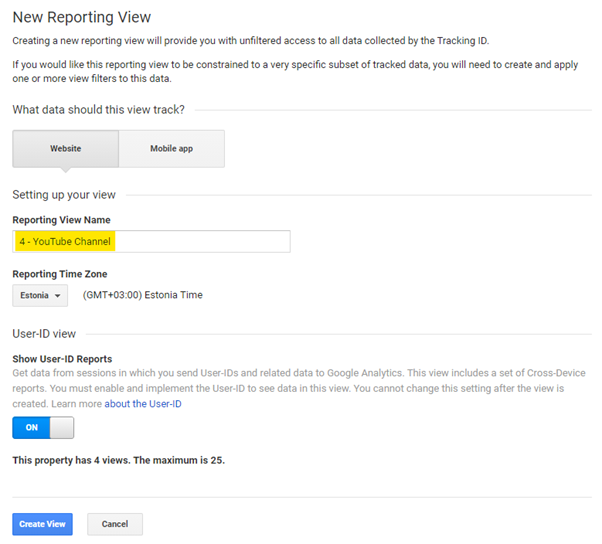
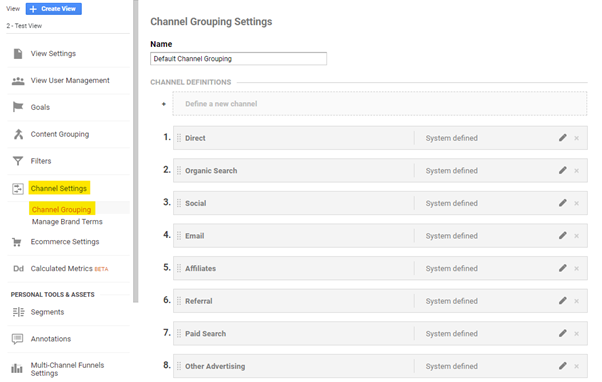
06Channel Settings
Channel Settings allows you to configure groupings for different channels. This information is displayed in the channel category-based reports. The need for this setup is rather small, but for some projects, it may be a justified step. For example, measuring traffic to a podcast or YouTube.
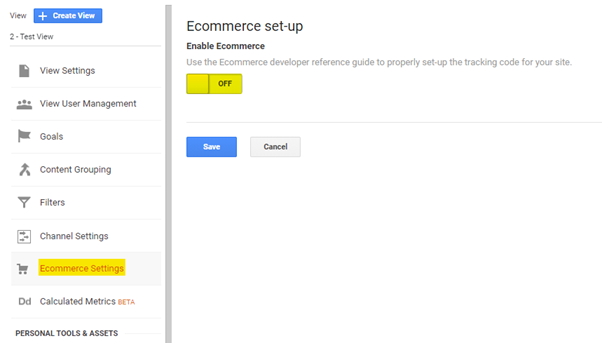
07E-commerce Settings
Ecommerce is wise to turn on if you have an e-commerce site. This will give you a complete overview of what the e-store is doing.
1) You need to turn on Ecommerce Settings
2) If your e-shop uses a third-party shopping cart system (located on a different domain) or you need to track transactions between different domains, you need to set up cross-domain tracking. If the shopping cart is on the same domain as the e-shop, you do not need to do so. More information about cross-domain-tracking can be found HERE.
3) To collect e-commerce information, you need to add JavaScript code to your page, which sends information about transactions and product information to Analytics. Find out more here.

















